Reasoning - Puzzles
Puzzle is considered as the toughest part of reasoning. In these days, various nation-wide exams are being conducted each year whether it is management entrance exams like CAT, XAT, MAT or bank selection exams like IBPS, SBI, RBI or any other exam. There is reasoning part and reasoning questions cannot be completed until there are puzzle questions.
Management entrance exams are high on puzzle questions. Especially, in CAT and XAT, the difficulty level of puzzle in reasoning is very high. In bank exams, normally there are a mix of all types of reasoning questions in the reasoning section. But in recent years, banks have shown their love towards puzzle. If a reasoning section in bank exams contains fifty questions then there are a minimum of 30 questions which are of puzzle type. Hence, in recent years whether it is management or any bank or PSU exam, puzzle is an important section of reasoning.
Puzzle is mainly of following types −
- Sitting arrangement (circular or rectangular)
- Sitting arrangement (facing towards north or south)
- Sitting arrangement (row I and row II facing each other)
- Blood relation
- Analytical reasoning
- Arithmetical reasoning
Sitting arrangement (circular and rectangular)
In these types of problems, a group of people sit around a circular table or a rectangular table. Then different types of arrangements are given in the questions. We have to read the question carefully and try to figure out what should be the exact sequence of sitting arrangement. Then put it on the circle or table which is given and find the answer.
Circular Arrangement Puzzle Based Questions and Answer
Circular Arrangement problems are a type of seating arrangement problems in which some people are sitting around a circular table either facing the centre or facing away from the centre. It is an important topic as you can expect 5 questions from this topic in Pre & Mains exams.
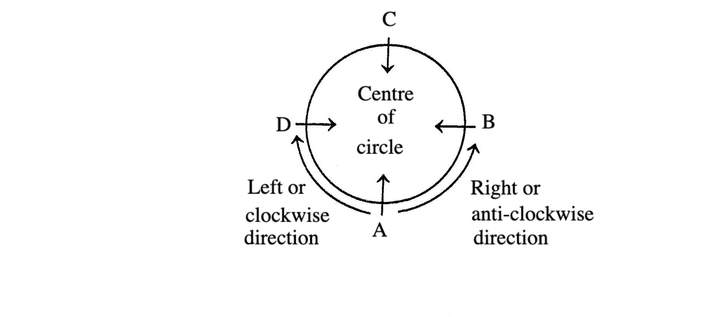
Facing Towards the Centre
Suppose A, B, C and D are four persons facing towards the centre, then their right and left sides are shown by the arrows in the given diagram. B is on the right side of A and D is on the left side of A.
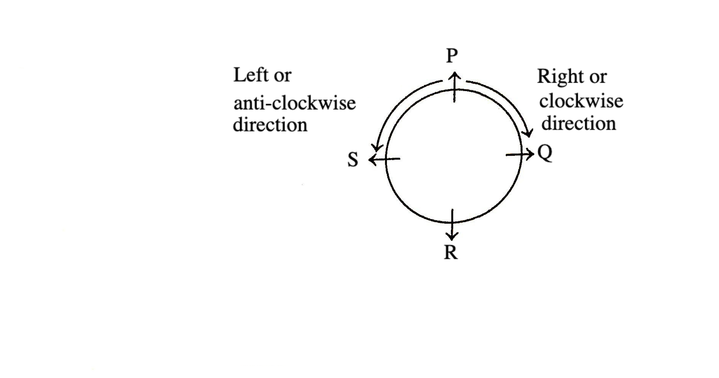
Facing Outside the Centre
Suppose there are four persons P, Q, R and S. All the persons are facing outside the centre, then their left and right sides are shown in the diagram by arrows. Q is on the right of P and S is on the left of P.
Example 1: Five students are standing in a circle. Abhinav is between Alok and Ankur. Apurva is on the left of Abhishek. Alok is on the left of Apurva. Who is sitting next to Abhinav on his right?
(a) Apurva (b) Ankur
(c) Abhishek (d) Alok
Solution: (d) We arrange the following students in a circle based on the information given in the question.
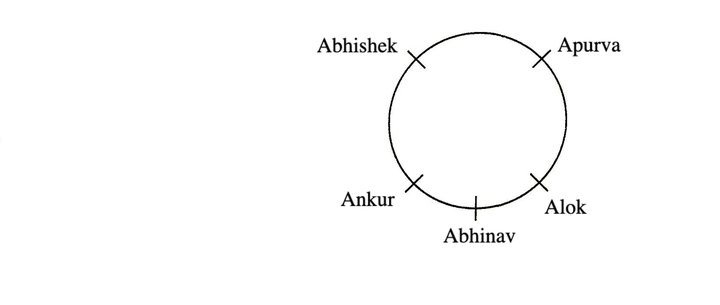
Clearly, Alok is sitting next of Abhinav on his right.
Directions (1-5): Circular arrangement puzzle based questions:
P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are eight individuals sitting around a circular table facing the centre.
P is second to the right of T who is the neighbour of R and V.
S is not the neighbour of P.
V is the neighbour of U.
Q is not between S and W.
W is not between U and S.
- Which two of the following are not immediate neighbors?
(a) RV
(b) UV
(c) RP
(d) QW
(e) None of these
- Which one is immediate right to the V?
(a) P
(b) U
(c) R
(d) T
(e) None of these
- Which of the following is true with respect to the seating arrangement?
(a) P is to the immediate right of Q
(b) R is between U and V
(c) Q is to the immediate left of W
(d) U is between W and S
(e) None of these
- What is the position of S?
(a) Between U and V
(b) Second to the right of P
(c) To the immediate right of W
(d) Data inadequate
(e) None of these
- Who is sitting second to the right of P?
(a) Q
(b) W
(c) S
(d) U
(e) V
Step 1:

P is second to the right of T who is the neighbour of R and V.
Step 2:

S is not the neighbour of P.
V is the neighbour of U.
Step 3:

Q is not between S and W.
W is not between U and S.
Answer
- (a)
- (d)
- (c)
- (c)
- (b)
Eight persons are sitting around a rectangular table in the given below manner.
![]()
Note: There are only two directions one is inward (towards center) and other is outward (away from center)
Not more than 3 persons are sitting between S and R from the right of
S. C is not immediate neighbour of S and is not facing towards centre. B
sits third to the right of A which is second to the left of Q. Q and C
are immediate neighbours of each other and both are facing same
direction. P and B are not an immediate neighbours of R. Not more than 1
persons are sitting between B and D from the left of B. P is not an
immediate neighbours of D. B and D are not facing the same direction.
Two persons are sitting between P and C and both are facing same
direction.
1. What is the position of C according to S?
A. Second to the right
B. Immediate left
C. Second to the left
D. Immediate right
E. None of the these
2. How many persons are sitting between R and A if counting from the right of R?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
E. Zero
3. Which statement is correct according to the arrangement?
A. D sits second to the right of P
B. C and S are immediate neighbours of each other
C. Q and S are facing the same direction
D. R sits immediate right of D
E. All of them correct
4. Which statement is not correct according to the arrangement?
A. R sits third to the left of A
B. P and S are immediate neighbours of each other
C. S and A are not facing the same direction
D. D sits immediate left of B
E. None of them correct
Sitting arrangement (facing towards north or south)
This another type of sitting arrangement in which a group of people or students sit on a straight line facing north or south direction. Then different types of arrangements are given in the question. We have to read the question carefully and try to figure out what should be the exact sequence of sitting arrangement. Then put it on the straight line and arrange their faces towards north or south which is given and find the answer.
• When it is not given in the question that in which direction the person(s) is facing, then we assume it facing the North direction.
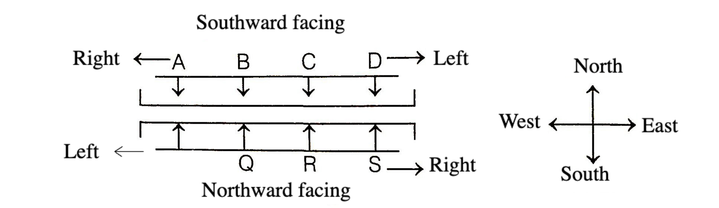
• When A, B, C and D are facing in South direction and P, Q, R and S are facing in North direction in a line, the positions to their right and left will be
• When A, B are in one line and P, Q in other, then diagonally opposite directions will be
A is diagonally opposite to Q and B is diagonally opposite to P.
Example 1: P, Q, R, S and T are sitting in a line facing West. P and Q are sitting together. R is sitting at south end and S is sitting at North end. T is neighbour of Q and R. Who is sitting the middle?
(a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S
Solution: (b) According to the given information, the sitting arrangement is a given below.
Clearly, from the above diagram, Q is setting in the middle.
Directions (Example Nos. 2-5) Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Six friends A, B, C, D, E and F are sitting in a row facing towards North. C is sitting between A and E. D is not at the extreme end. B is sitting at immediate right of E. F is not at the right end but D is sitting at 3rd left of E.
Example 2: How many persons are there to the right of D?
(a) One (b) Two (c) Three (d) Four (e) None of these
Example 3: Which of the following is setting to the left of D?
(a) F (b) C (c) E (d) A (e) None of these
Example 4: Who is at the immediate left of C?
(a) A (b) E (c) Either E or A
(d) Cannot be determined
(e) None of these
Example 5: Who is at the right end?
(a) A (b) B (c) E
(d) Cannot be determined
(e) None of these
Solution: (Example Nos. 2-5) According to the given information, the sitting arrangement of six friends is as given below

2. (d) It is clear from the diagram that there are four persons to the right of D ----- A, C, E and B.
3. (a) It is clear from the diagram that F is sitting to the left of D.
4. (a) It is clear from the diagram that A is at the immediate left of C.
5. (b) It is clear from the diagram that B is at the right end.
Example 6: Six persons A, B, C, D, E and F sit in two rows of three persons each. If E is not at any end of rows, D is second to the left of F, C is the neighbour of E and is sitting diagonally opposite to D and B is the neighbour of F, then who will sit opposite B?
(a) A (b) E (c) C (d) D
Solution: (b) According to the given question, the arrangements are as follows
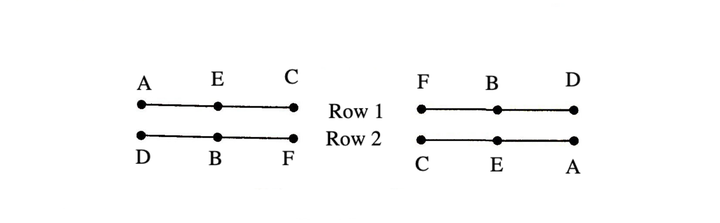
Hence, E is sitting opposite to B.
Note : Linear arrangement also includes floor arrangement in which people are arranged as per their floor numbers from top to bottom. The lowest floor is usually numbered 1.
Directions (Example Nos. 7-9) Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
There are eight persons namely S, T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z lives on eight different floors from one to eight. Ground floor is number one and one above that is number two and so on till the topmost floor is number eight. X lives on odd number floor but does not live on 3rd floor. Z lives immediate below X. More than two person lives between Z and Y. There are six person lives between S and Y. V lives immediate above W, but live below T. U does not live above X. W does not live immediate above Y.
Example 7: Who lives on floor number five?
(a) U (b) S (c) Z (d) T (e) None of these
Example 8: How many persons live between W and X?
(a) One (b) Three (c) Five (d) Two (e) None of these
Example 9: Who lives immediately above V?
(a) Z (b) T (c) Y (d) W (e) None of these
Solution: (Example Nos. 7-9) According to the given information, the arrangement is as follows
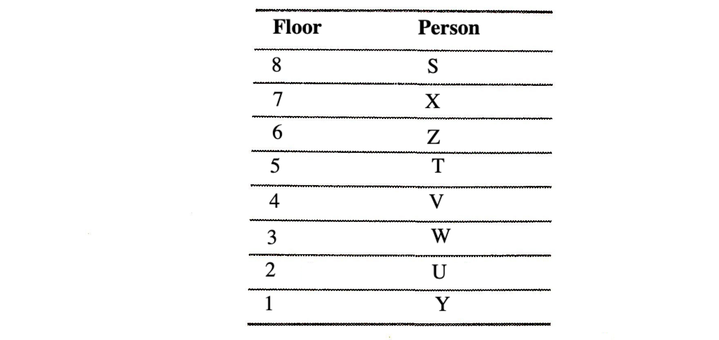
7. (d) T lives on floor number five.
8. (b) Three person live between W and X.
9. (b) T lives immediately above V.
Sitting arrangement (row I and row II facing each other)
This is a different type of sitting arrangement in which there may be four to five people in each row and they face each other. Normally in these questions, the people in row I face south and the people of row II face north. In this way theyface each other. Then different types of arrangements are given in the question. We have to read the question carefully and try to figure out what should be the exact sequence of sitting arrangement. Then put them on row I or row II which is given and find the answer.


Directions: (1-5) Answer the questions based on the information given below:
Eight friends i.e. J, K, P, Z, C, B, D,
and G have decided to do the lunch in a restaurant. They have seated on
two parallel rows, each having five seats. Each row has one vacant seat
but those vacant seats are not opposite to each other. P, C, Z and D sit
in row 1 and face South, whenever J, K , G and B sit in row 2 and faces
North. They like different colors i.e. Blue, Green, Grey, Black, Red,
Yellow, White and Pink, but not necessary in same order.
The one who likes Grey sits 2nd right of G but both do not sit at any
extreme end. The one who faces the one, who likes Grey, sits immediate
left of the vacant seat of row 1. There is only one person sits between
vacant seat of row 2 and J. The one who faces the vacant seat of row 2
is C who likes Yellow. P sits 3rd right of C. The one who likes Blue is
immediate neighbor of the one who faces P. The one who likes green faces
the one who likes Blue. K does not like Blue. Z does not like Green.
The one who likes white faces vacant seat of row 1. The one, who likes
Pink sits second to the right of the one who likes Red.
1.Who among the following likes White?
A. B
B. K
C. Z
D. C
E. J
2.Who among the following sits 2nd left of the one who likes Green?
A. B
B. K
C. Z
D. No one
E. P
3.Who among the following likes Black?
A. C
B. D
C. P
D. B
E. G
4.Who among the following faces the one who likes Red?
A. B
B. K
C. Z
D. C
E. P
5.How many person sit between G and J?
A. Two
B. One
C. Four
D. Three
E. None
Directions:(6-10) Answer the questions based on the information given below.
Twelve persons sitting on two parallel rows ie. In Row-1 I, J, K, L, M and N are sitting facing North and In Row-2 P, Q, R, S, T and U are sitting facing South, but not necessarily in the same order. Each one in a row is facing exactly another one from the other row. P sits second to the right of the person who sits opposite J. J does not sit at any end of the row. K and L are immediate neighbors of J, and one of them sits at an extreme end. M sits second to the left of L but not opposite R. P is a neighbor of R but is not opposite N. Neither Q nor T are adjacent to P. T is adjacent to either R or Q but not both. U is a neighbor of the person who sits opposite M.
6.Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and so form a group. Find the one which does not belong to that group?
A. U, I
B. P, J
C. L, S
D. K, R
E. L, T
7.Which of the following is true, according to the given information?
A. U and K are at the extremes ends.
B. R sits second to the right of S.
C. T sits to the immediate right of Q.
D. J sits second to the left of I.
E. All the above
8.Who sits opposite K?
A. S
B. P
C. R
D. Q
E. T
9.Who sits second to the left of R?
A. S
B. T
C. P
D. Q
E. U
10.If S and L interchange their positions, then who sits to the immediate left of L?
A. U
B. R
C. P
D. T
E. Q
Blood Relation
In blood relation types of questions, normally two to three generation of a family is given and their names are given. We have to read the question and find the correct order of family tree. The blood relation questions come for just two to three marks. But for five or more than five marks, the blood relation question is normally different. It is not as easy as the above mentioned types of puzzles but a little more inspection can do the trick. For higher blood relation puzzles, along with family tree, the profession of each person is also added. So we have to look each case carefully and the profession along with the relation of the given persons.
Tips:
Indicate – for Female candidate
Indicate <=> for Couple
Indicate - - - - for Same Generation like brother - - - brother (or) sister - - - sister (or) sister - - -brother
Indicate–––––for Different generations like father–––––son (or) mother––––son (or) father––––daughter (or) Mother ––––– daughter
Mother's or father's daughter→ Sister
Mother's or father's brother→ Uncle
Mother's or father's sister→ Aunt
Mother's or father's father→ Grandfather
Mother's or father's mother→ Grandmother
Son's wife→ Daughter-in-law
Daughter's husband→ Son-in-law
Husband's or wife's sister→ Sister-in-law
Husband's or wife's brother→ Brother-in-law
Brother's son→ Nephew
Brother's daughter→ Niece
Uncle or aunt's son or daughter→ Cousin
Sister's husband→ Brother-in-law
Brother's wife→ Sister-in-law
Grandson's or Granddaughter's daughter→ Great Grand daughter
Besides that, blood relation is attached with sitting arrangement and analytical reasoning. Such type of questions are frequently asked in the exams nowadays. These questions are normally time-taking and normally carry maximum marks.
A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circle facing the
centre but not necessarily in the same order. Each of them has a
relationship with A.
G is sitting second to the left of father of A. F is immediate neighbor
of A. D, mother of A is sitting opposite to the sister of A. B is
sitting to the immediate right of wife of A. E who is a male is sitting
second to the right of mother of C. Brother of A is sitting third to
right of B. Daughter of A is sitting to third to right of sister of A. A
is sitting second to the right of daughter of E. E is sitting to the
immediate left of sister of A.
- Who is the mother of H?
A) F
B) G
C) C
D) D
E) None of these
- Who is the grand-daughter of E?
A) B
B) C
C) D
D) G
E) None of these
- Who is sitting second to the right of F’ sister?
A) wife of A
B) brother of C
C) daughter of A
D) father of B
E) None of these
- How many persons are sitting between A’s wife and D’s husband when counted from right of A’s wife?
A) None
B) One
C) Two
D) Three
E) More than three
- What is the position of G’s daughter with respect to D’s daughter?
A) third to left
B) second to left
C) third to right
D) second to right
E) fourth to right
Analytical Reasoning
After blood relation, analytical reasoning is the most asked question in reasoning. This is normally represented in tables. As the name suggests, these are analysis based reasoning questions. We have to analyse these questions deeply. Practice is the only key to tame such questions.
#1 -Maths Brain Twister Puzzle
A research team went to a village somewhere between the jungles of
Africa. Luckily for them, they reached on the day when quite an
interesting custom was to be performed. The custom was performed once in
a year as they confirmed and was performed in order to collect the
taxes from every male of the region.
The taxes were to be paid in the form of grains. Everyone must pay
pounds of grain equaling his respective age. Which means a 20 year old
will have to pay 20 pounds of grains and a 30 years old will pay 30
pounds of grain and so on.
The chief who collects the tax have 7 weights and a large 2 pan scale to
weigh. But there is another custom that the chief can weigh only with
three of the seven weights.
Can you find out the weights of the seven weights? Also what is the
maximum age of the man that can be weighed for the payment of taxes ?

There is a thing which you must keep in mind. The chief can put weights on both the pans.
Keeping that in mind
The weights 1, 3, 7, 12, 43, 76, 102
The oldest age that can be measured with these weights is 122
#2 - Hard River Crossing Logic Puzzle
You must have heard of so many river crossing riddles however this one
is a bit tricky one. We have a dysfunctional family on one side of the
river which includes mom and 2 daughters, dad and 2 sons, a maid and a
dog. Like usual, there is a boat that can hold only two persons at a
time (dog counts as one person as well). Obviously, the kids can’t
operate the boat and we need an adult for that task.
Here comes the difficulties. The maid must remain with the dog so she
can control it or it will head up for a violent biting. The dad cannot
be left with the daughters without mom and nor can the mother be left
alone with the sons without dad.
Can you help them cross the river?

Suppose that everyone is standing at A corner and they have to reach the B corner
Let the housemaid and Dog go to corner B first and housemaid returns back to corner A.
Next, the housemaid and the first son go to B and she comes back along with the dog.
Now the father and the second son go to B and father comes back.
Mother and Father go to B and the mother comes back.
Housemaid and Dog go to B and the father comes back.
Father and mother goes to B and Mother returns back.
Mother and first daughter go towards B, Housemaid and Daughter returns back.
Housemaid and second Daughter go to B and Housemaid comes back.
Housemaid and Dog goes to B.
So, everyone has reached the other side of the river successfully.
FOR MORE EXAMPLES REFER:http://www.briddles.com/riddles/analytical-reasoning
Arithmetical Reasoning






Comments
Post a Comment